Retinoid X receptor beta
| RXRB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | RXRB, DAUDI6, H-2RIIBP, NR2B2, RCoR-1, Retinoid X receptor beta, RXRbeta, RXR-beta | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 180246; MGI: 98215; HomoloGene: 7923; GeneCards: RXRB; OMA:RXRB - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Retinoid X receptor beta (RXR-beta), also known as NR2B2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group B, member 2) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRB gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a member of the retinoid X receptor (RXR) family of nuclear receptors which are involved in mediating the effects of retinoic acid (RA). This receptor forms heterodimers with the retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors, increasing both DNA binding and transcriptional function on their respective response elements. The gene lies within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II region on chromosome 6. An alternatively spliced transcript variant has been described, but its full length sequence has not been determined.[6]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
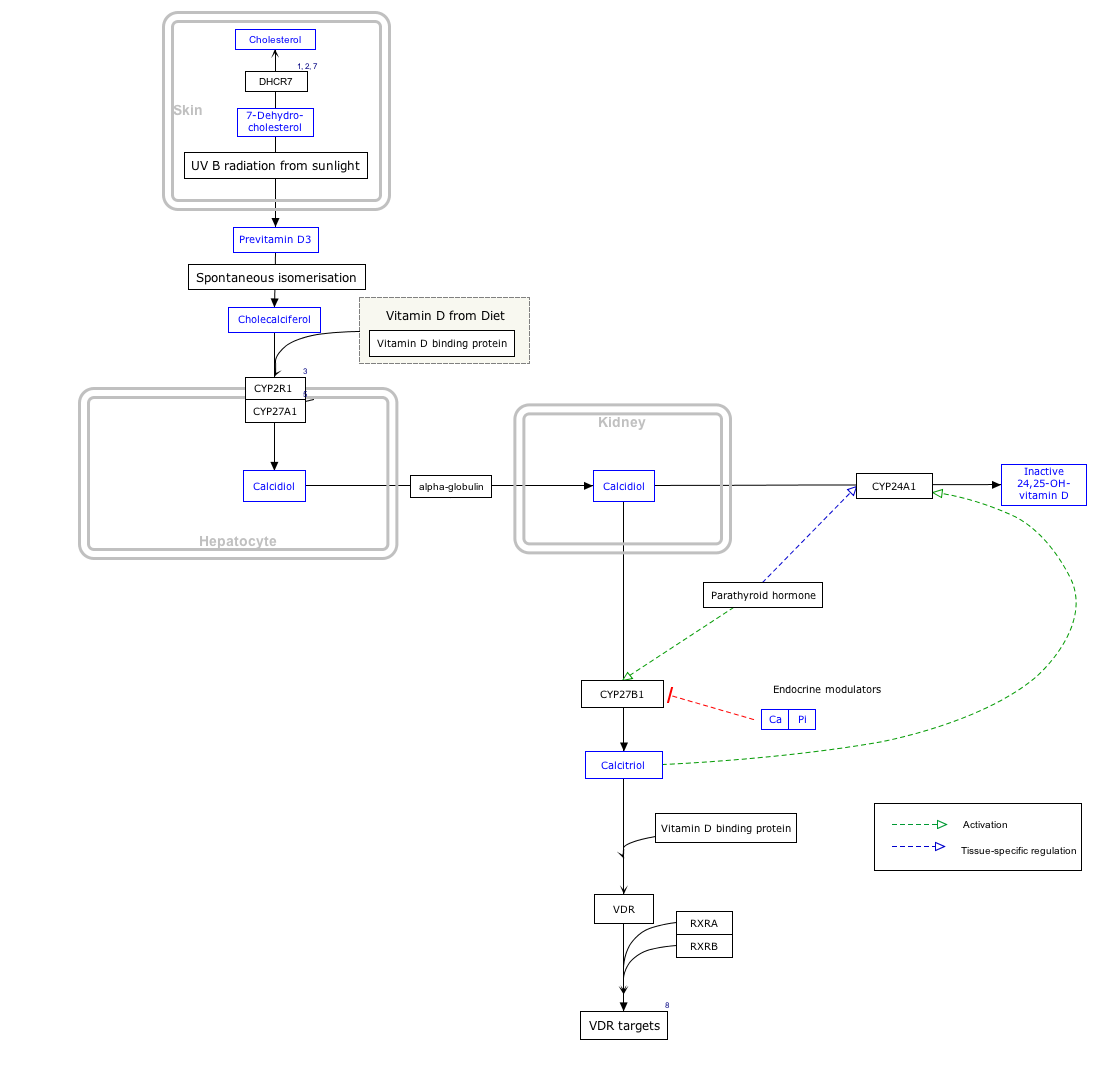

- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
See also
References
- ^ a b c ENSG00000231321, ENSG00000227322, ENSG00000204231, ENSG00000206289, ENSG00000228333 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000235712, ENSG00000231321, ENSG00000227322, ENSG00000204231, ENSG00000206289, ENSG00000228333 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000039656 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Fitzgibbon J, Gillett GT, Woodward KJ, Boyle JM, Wolfe J, Povey S (Jul 1993). "Mapping of RXRB to human chromosome 6p21.3". Annals of Human Genetics. 57 (Pt 3): 203–9. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1993.tb01596.x. PMID 8257090. S2CID 26964941.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: RXRB retinoid X receptor, beta".
Further reading
- Szanto A, Narkar V, Shen Q, Uray IP, Davies PJ, Nagy L (Dec 2004). "Retinoid X receptors: X-ploring their (patho)physiological functions". Cell Death and Differentiation. 11 (Suppl 2): S126–43. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401533. PMID 15608692.
- Leid M, Kastner P, Lyons R, Nakshatri H, Saunders M, Zacharewski T, Chen JY, Staub A, Garnier JM, Mader S (Jan 1992). "Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently". Cell. 68 (2): 377–95. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-U. PMID 1310259. S2CID 40617478.
- Fleischhauer K, Park JH, DiSanto JP, Marks M, Ozato K, Yang SY (Apr 1992). "Isolation of a full-length cDNA clone encoding a N-terminally variant form of the human retinoid X receptor beta". Nucleic Acids Research. 20 (7): 1801. doi:10.1093/nar/20.7.1801. PMC 312273. PMID 1315958.
- Berrodin TJ, Marks MS, Ozato K, Linney E, Lazar MA (Sep 1992). "Heterodimerization among thyroid hormone receptor, retinoic acid receptor, retinoid X receptor, chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor, and an endogenous liver protein". Molecular Endocrinology. 6 (9): 1468–78. doi:10.1210/mend.6.9.1331778. PMID 1331778. S2CID 24291055.
- Epplen C, Epplen JT (1992). "The human cDNA sequence homologous to the mouse MHC class I promoter-binding protein gene contains four additional codons in lymphocytes". Mammalian Genome. 3 (8): 472–5. doi:10.1007/BF00356161. PMID 1514958. S2CID 1278904.
- Yu VC, Delsert C, Andersen B, Holloway JM, Devary OV, Näär AM, Kim SY, Boutin JM, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (Dec 1991). "RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements". Cell. 67 (6): 1251–66. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-E. PMID 1662118. S2CID 10354699.
- Oñate SA, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW (Nov 1995). "Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily". Science. 270 (5240): 1354–7. Bibcode:1995Sci...270.1354O. doi:10.1126/science.270.5240.1354. PMID 7481822. S2CID 28749162.
- Kooistra T, Lansink M, Arts J, Sitter T, Toet K (Sep 1995). "Involvement of retinoic acid receptor alpha in the stimulation of tissue-type plasminogen-activator gene expression in human endothelial cells". European Journal of Biochemistry. 232 (2): 425–32. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.425zz.x. PMID 7556191.
- Perlmann T, Jansson L (Apr 1995). "A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1". Genes & Development. 9 (7): 769–82. doi:10.1101/gad.9.7.769. PMID 7705655.
- Forman BM, Umesono K, Chen J, Evans RM (May 1995). "Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors". Cell. 81 (4): 541–50. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90075-6. PMID 7758108. S2CID 3203590.
- Zanaria E, Muscatelli F, Bardoni B, Strom TM, Guioli S, Guo W, Lalli E, Moser C, Walker AP, McCabe ER (Dec 1994). "An unusual member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily responsible for X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita". Nature. 372 (6507): 635–41. Bibcode:1994Natur.372..635Z. doi:10.1038/372635a0. PMID 7990953. S2CID 4363344.
- Almasan A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Ong ES, Wahl GM, Evans RM (Apr 1994). "Chromosomal localization of the human retinoid X receptors". Genomics. 20 (3): 397–403. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1193. PMID 8034312.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (Jan 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Fleischhauer K, McBride OW, DiSanto JP, Ozato K, Yang SY (Jan 1993). "Cloning and chromosome mapping of human retinoid X receptor beta: selective amino acid sequence conservation of a nuclear hormone receptor in mammals". Human Genetics. 90 (5): 505–10. doi:10.1007/BF00217449. PMID 8381386. S2CID 26472949.
- May M, Mengus G, Lavigne AC, Chambon P, Davidson I (Jun 1996). "Human TAF(II28) promotes transcriptional stimulation by activation function 2 of the retinoid X receptors". The EMBO Journal. 15 (12): 3093–104. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00672.x. PMC 450252. PMID 8670810.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (Sep 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Joyeux A, Cavaillès V, Balaguer P, Nicolas JC (Feb 1997). "RIP 140 enhances nuclear receptor-dependent transcription in vivo in yeast". Molecular Endocrinology. 11 (2): 193–202. doi:10.1210/mend.11.2.9884. PMID 9013766.
- Xu XC, Sozzi G, Lee JS, Lee JJ, Pastorino U, Pilotti S, Kurie JM, Hong WK, Lotan R (May 1997). "Suppression of retinoic acid receptor beta in non-small-cell lung cancer in vivo: implications for lung cancer development". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 89 (9): 624–9. doi:10.1093/jnci/89.9.624. PMID 9150186.
- Chen H, Lin RJ, Schiltz RL, Chakravarti D, Nash A, Nagy L, Privalsky ML, Nakatani Y, Evans RM (Aug 1997). "Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300". Cell. 90 (3): 569–80. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80516-4. PMID 9267036. S2CID 15284825.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
- v
- t
- e
-
 1by4: STRUCTURE AND MECHANISM OF THE HOMODIMERIC ASSEMBLY OF THE RXR ON DNA
1by4: STRUCTURE AND MECHANISM OF THE HOMODIMERIC ASSEMBLY OF THE RXR ON DNA -
 1dsz: STRUCTURE OF THE RXR/RAR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN HETERODIMER IN COMPLEX WITH THE RETINOIC ACID RESPONSE ELEMENT DR1
1dsz: STRUCTURE OF THE RXR/RAR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN HETERODIMER IN COMPLEX WITH THE RETINOIC ACID RESPONSE ELEMENT DR1 -
 1h9u: THE STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN RETINOID-X-RECEPTOR BETA LIGAND BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH THE SPECIFIC SYNTHETIC AGONIST LG100268
1h9u: THE STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN RETINOID-X-RECEPTOR BETA LIGAND BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH THE SPECIFIC SYNTHETIC AGONIST LG100268 -
 1r0n: Crystal Structure of Heterodimeric Ecdsyone receptor DNA binding complex
1r0n: Crystal Structure of Heterodimeric Ecdsyone receptor DNA binding complex -
 1rxr: HIGH RESOLUTION SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE RETINOID X RECEPTOR DNA BINDING DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURE
1rxr: HIGH RESOLUTION SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE RETINOID X RECEPTOR DNA BINDING DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURE -
 1uhl: Crystal structure of the LXRalfa-RXRbeta LBD heterodimer
1uhl: Crystal structure of the LXRalfa-RXRbeta LBD heterodimer -
 2nll: RETINOID X RECEPTOR-THYROID HORMONE RECEPTOR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN HETERODIMER BOUND TO THYROID RESPONSE ELEMENT DNA
2nll: RETINOID X RECEPTOR-THYROID HORMONE RECEPTOR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN HETERODIMER BOUND TO THYROID RESPONSE ELEMENT DNA
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 6 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e